Predicting changes in cardiac myocyte contractility during early drug discovery with in vitro assays
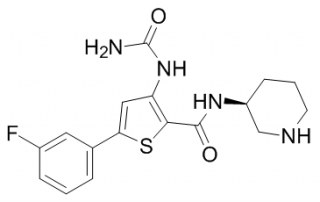
Predicting changes in cardiac myocyte contractility Abstract: Cardiovascular-related adverse drug effects are a major concern for the pharmaceutical industry. Activity of an investigational drug at the L-type calcium channel could manifest in a number of ways, including changes in cardiac contractility. The aim of this study was to define [...]