ApconiX Case studies

The Effect of Intracellular pH on hERG Inhibition
Cynara Livera2023-09-28T11:44:24+01:00The effect of intracellular pH on hERG inhibition
The challenge
A valued client, BugWorks Research, approached ApconiX to help them investigate the effect of intracellular pH on the inhibition of hERG potassium channel. At different pH, molecules might carry a different charge, depending on their structure. This may affect the molecule’s activity at hERG. Their enquiry followed some unexpected hERG inhibition by their compounds and the discovery of a paper published in 2016 by Wang et al. The paper showed that dofetilide, a known hERG blocker, had a quicker onset of effect at lower intracellular pH than under standard conditions. As shown in Figure 1.
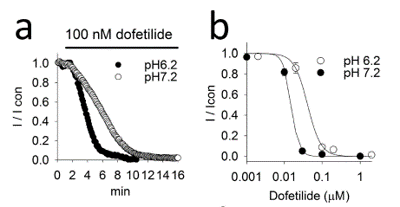
Figure 1: Decreased time to effect of dofetilide at intracellular pH 6.2 versus pH 7.2 (from Wang et al., 2016)
The science
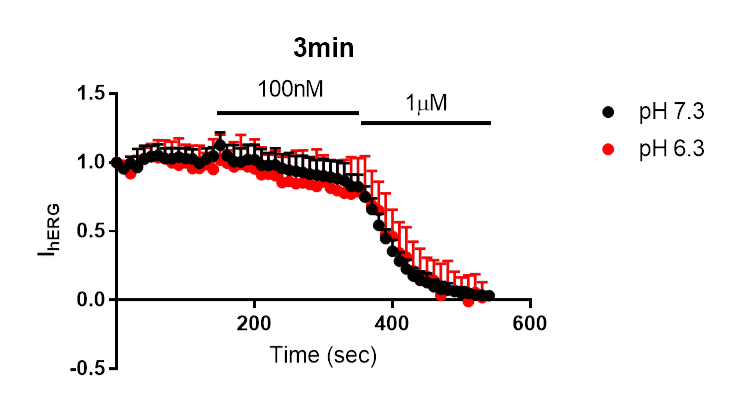
Electrophysiology experiments were performed on the Patchliner automated patch-clamp system (Nanion Technologies). These experiments showed no significant difference in the onset of dofetilide inhibition at lower intracellular pH, as illustrated in figure 2.
There is limited literature in this area. ApconiX found a second paper by Du et al., 2011, which reported no effect of intracellular pH on hERG inhibition by dofetilide, contesting Wang’s original data.
The outcome
Based on data from ApconiX and others, it is unlikely that intracellular pH is affecting the onset of hERG inhibition. Changes in intracellular pH that might affect the charge of a molecule does not, in this case, explain unexpected hERG inhibition.
Du et al (2011) Enhanced inhibitory effect of acidosis on hERG potassium channels that incorporate the hERG1b isoform. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 405, 222–7
Wang et al. (2016) Role of the pH in state-dependent blockade of hERG currents. Scientific Reports 6: 32536
The Testimonial
“Your data turnaround time is incredibly good and it really helps us track the SAR and progress our compounds in a rapid and efficient manner. Thanks ApconiX for your wonderful support to Bugworks.”