Phumzile Sikakana Celebrates a Few Firsts: First Paper as First Author and First Paper with ApconiX

It’s great to have something to celebrate this year and ApconiX was delighted to hear Phumzile Sikakana had her first paper published with ApconiX. It was also Phum’s first, first author paper!
A Decade of Toxicological Trends: What the Papers Say: download the free access paper here:
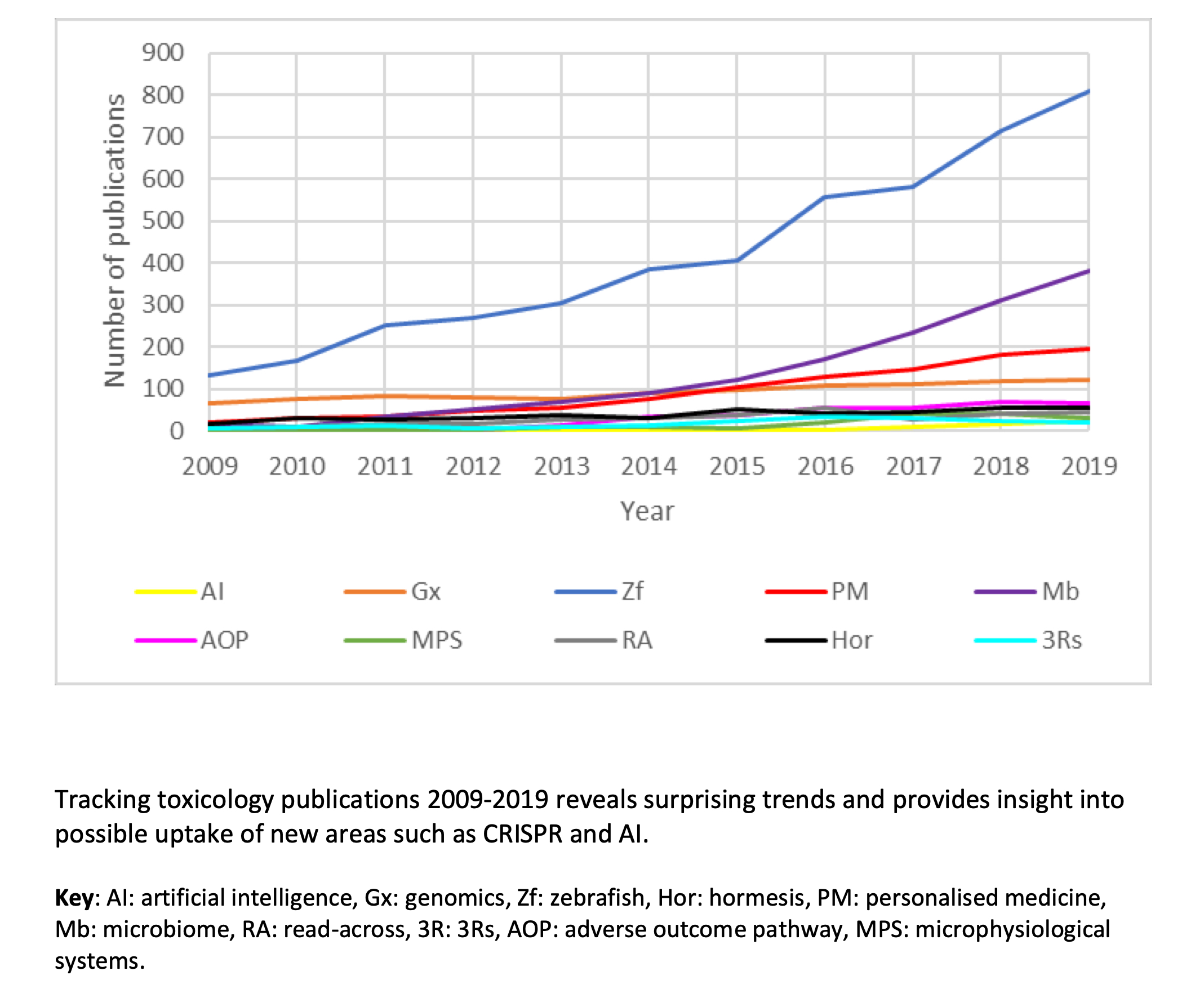
Professor Ruth Roberts, Director and Co-founder of ApconiX, commented, “We were just talking about trends in toxicology and how interesting they are – then the idea came up of tracking trends via publications. The results surprised us too! The top slots (Zebrafish, Genomics and Personalised Medicine) have been relatively static over recent years – this suggests a degree of continuity despite the noise around emerging new trends such as artificial intelligence, microphysiological systems and the microbiome”.
Phum added, “Being relatively new to the toxicology field, it was interesting to do some research into the trends over the last decade and think to the future of where we might be headed. It was great to have the chance to write a reflective viewpoint article that could repeated in the future to see how our predictions pan out”.
Graphical Abstract:
Abstract:
Here we look at popular trends and concepts in toxicology over the decade 2009–2019. The top 10 concepts included methodological approaches such as zebrafish and genomics as well as broader concepts such as personalized medicine and adverse outcome pathways. The total number and rank order for each of the top 10 were tracked year by year via PubMed with >9500 papers contributing to the analysis. The data revealed a slow upward trend in the number of papers across all the concepts from 260 in 2009 to >1700 in 2019. Zebrafish, genomics and personalized medicine remained in the top four slots since 2009 with zebrafish dominating the rankings over the entire decade. Genomics was a strong second until 2013 when it was displaced first by the microbiome in 2014 and secondly by personalized medicine in 2015. Other notable trends were the ascendancy of the microbiome and adverse outcome pathways and the descendancy of hormesis and the 3Rs (replacement, reduction and refinement of animals in testing). The observation that the top four slots have been static over the past 4 years suggests that new ideas are introduced and increase in popularity until they find their place in scientific culture. This may suggest that relatively new concepts such as artificial intelligence and microphysiological systems have yet to find their steady state in the rankings. Similarly, as a relatively new player in toxicology, the full impact of the human microbiome on drug efficacy and safety remains to be seen.